Prostatitis
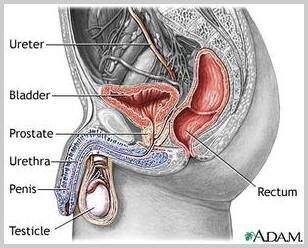
Prostatitis is the term used for inflammation of the prostate gland commonly resulting in pain and swelling.The prostate gland is part of the male reproductive system. It is a gland located below the bladder and surrounds the urethra and sits in front of the rectum. The condition of prostatitis can also cause other uncomfortable urinary symptoms which can be chronic or acute, and flare-up irregularly. Symptoms can range from mild to very severe.
Causes of Prostatitis
Most acute cases are caused by an infection of the prostate gland, while chronic or recurrent cases do not usually have a clear cause, but may be the consequence of:
• A bacterial infection
• Traumatic injury to the prostate
• Prior catheter insertion
• Sexually transmitted diseases
• Abnormal pelvic nerves
• There may be genetic component
Symptoms of Prostatitis
Symptoms experienced with prostatitis are similar to other types of urinary tract infections. Common symptoms of prostatitis may be:
● Difficulty and pain while urinating (dysuria)
● Urinary tract infections
● Fever, chills
● Blood in urine
● Feeling of unable to empty bladder
● Groin pain, lower abdominal pain
● Lower back pain
● Sexual dysfunction
Diagnosis of Prostatitis
Diagnosis may involve ruling out the possibility of other conditions. To diagnose prostatitis, the following tests may be performed as well as gathering history and a physical exam:
● Urinalysis
● Testing of prostate fluids/semen culture
● Digital rectal exam to feel for prostate tenderness
● Cystoscopy
● Prostate specific antigen test or PSA
Types of Prostate Infections
Prostatitis can be classified as one of the following types:
Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
Acute bacterial prostatitis is caused by a bacterial infection of the prostate. Symptoms such as fever, urinary discomfort and pain (dysuria), may appear immediately. It may be accompanied by fevers.
Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is another type of bacterial infection with symptoms that are less severe and show gradually. They may occur recurrently. Recurring urinary tract infections may be a sign of this type of prostatitis and may be a symptom of underlying prostate issue
Nonbacterial Prostatitis
Nonbacterial prostatitis is the most common type of prostatitis and it may be caused by persistent inflammation or infection. Symptoms may include urinary pain or discomfort or there may be no symptoms at all.
Treatment of Prostatitis
Treatment for prostatitis varies due to the cause and specific type of the condition, and may include:
● Antibiotics for infection
● Anti-inflammatory medication
● Hot baths
● Prostatic massage
● Increased ejaculation
● Nerve blocks
Left untreated, prostatitis can affect quality of life and it can lead to abnormal semen and infertility. While prostatitis can be a painful condition, it is treatable and if diagnosed correctly, patients can find relief from treatment.
